Now available at Breach Candy Hospital on Wednesdays 07:00 pm to 08:00 pm

Dr. Dilip Raja
Urologist & Andrologist
Male Infertility
Illnesses, injuries, chronic health problems, lifestyle choices and other factors can play a role in causing male infertility.
Get in touch with us today (022) 2645 2007
Male Infertility
- The American Society of Reproductive Medicine (ASRM) estimates that in about a third of infertility cases it is due to the male. Another third is the female. In the last third of infertile couples, the problem is caused by either a combination of reasons, or, in 20 out of 100 cases, it can’t be explained.
- Male infertility is any health issue in men that refers to a male’s inability to cause pregnancy in a fertile female. Male infertility is the result of low sperm production, abnormal sperm function or blockages that prevent the delivery of sperm. Illnesses, injuries, chronic health problems, lifestyle choices and other factors can play a role in causing male infertility. Hence, male infertility treatment in India has high demand. In metro cities like Mumbai, people consult infertility specialist in Mumbai to resolve the male infertility problem.

How do you know if your male partner has an infertility issue?
- Swelling and pain in the genital region
- Low sex desire
- Trouble getting an erection
- Retrograde ejaculation
Causes Of Male Infertility
- Hormonal imbalance:Increase or decrease in the amount of any hormone responsible for sperm production can cause infertility.
- Stress: Increased stress hormones can reduce the levels of testosterone and in turn, decrease the sperm count.
- Chromosomal abnormalities: Males with Klinefelter syndrome have an extra ‘X’ chromosome (XXY) in their genetic make-up. Such men will not have enough sperm or no sperms in their testes.
- Chromosomal abnormalities: Males with Klinefelter syndrome have an extra ‘X’ chromosome (XXY) in their genetic make-up. Such men will not have enough sperm or no sperms in their testes.
- Genetic conditions: A low sperm counts due to specific genetic conditions such as an autoimmune disease where your body produces antibodies that attack your sperm.
- Obesity: Being overweight can reduce the levels of testosterone hormone, thus affecting sperm quality and count.
- Blockage or obstruction: A block in the tubes that pass the ejaculate can prevent the delivery of the sperm.
- Lifestyle habits: Excess smoking, particularly marijuana or hash smoking, has shown to reduce sperm count, sperm quality or damage to the sperm DNA. Recent studies have proved that the offspring of couples with the excessive smoking habit can have a higher risk of childhood cancers. Excess alcohol consumption, using recreational drugs, eating unhealthy food also contribute to infertility.
- Injury or infection: Any trauma to the testis or testicular infection can cause the testis to stop producing the sperms.
- Other reasons: Chemotherapy or uncontrolled diabetes can affect sperm generation and quality. Sometimes the cause of infertility remains explained.
Some Of The Other Common Causes Of Male Infertility
- Sperm Disorders: Sperm problems can be from traits you’re born with. Lifestyle choices can lower sperm numbers. Smoking, drinking alcohol, and taking certain medications can lower sperm numbers. Other causes of low sperm numbers include long-term sickness (such as kidney failure), childhood infections (such as mumps), and chromosome or hormone problems (such as low testosterone).
- Varicoceles: Varicoceles are swollen veins in the scrotum. They harm sperm growth by blocking proper blood drainage. It may be that varicoceles cause blood to flow back into your scrotum from your belly. The testicles are then too warm for making sperm. This can cause low sperm numbers.
- Retrograde Ejaculation: Retrograde ejaculation is when semen goes backwards in the bladder. They go into your bladder instead of out the penis. This happens when nerves and muscles in your bladder don’t close during orgasm (climax). Semen may have normal sperm, but the semen cannot reach the vagina. Retrograde ejaculation can be caused by surgery, medications or health problems of the nervous system. Signs are cloudy urine after ejaculation and less fluid or “dry” ejaculation.
- Hormones: Hormones made by the pituitary gland tell the testicles to make sperm. Very low hormone levels cause poor sperm growth.
- Medication: Certain medications can change sperm production, function and delivery.
- arthritis
- depression
- digestive problems
- infections
- high blood pressure
- cancer
- Immunologic Infertility: Sometimes a man’s body makes antibodies that attack his own sperm. Antibodies are most often made because of injury, surgery or infection. They keep sperm from moving and working normally. This is not a common cause of male infertility. Prevention Many types of male infertility aren’t preventable.However, you can avoid some known causes of male infertility.
- Don’t smoke.
- Limit or abstain from alcohol.
- Steer clear of illicit drugs.
- Keep the weight off.
- Don’t get a vasectomy.
- Avoid things that lead to prolonged heat for the testicles.
- Reduce stress.
- Avoid exposure to pesticides, heavy metals and other toxins
Diagnosis Of Male Infertility
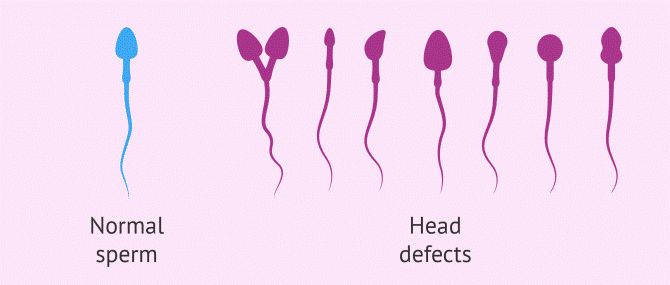
Semen analysis: It is a male fertility test that starts with a semen sample collection in a clean container. The male can masturbate and release the ejaculate completely keeping 05 days of abstinence. First few drops of the semen are very rich in sperms. Hence, you should carefully collect the semen and then give it for examination.An average sperm count is around 15 million to 200 million per ml of the ejaculate. Sperm count less than 15 million, we call oligospermia or low sperm count. Less than five million is severe oligospermia that means severely reduced sperm count. Not only the count but we also have to check the sperm motility, morphology and viability as it plays a significant role. All three functional parameters together to call a good sperm analysis.The morphology that is shape of the sperm head, or the sperm tail should be standard as it plays a vital role in attaching the egg. The sperm quality is examined under a high magnification microscope.
Analysis Of Hormonal Levels
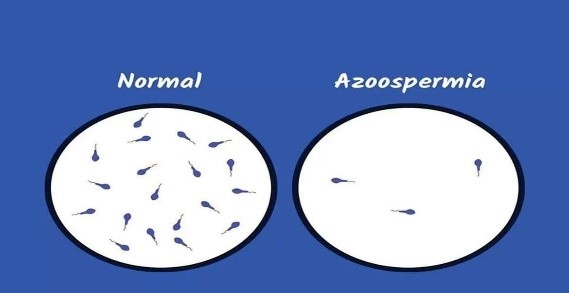
In a few cases, there is not even a single sperm in the ejaculate, i.e., Azoospermia. In such cases, we do a hormone analysis of the males. We check the testosterone level, the FSH, LH, Thyroid, etc.
- Ultrasound with Doppler studies for evaluation of Bilateral Varicocele: The third examination that you can do is an ultrasound of the testis. Ultrasound determines the structure and size of the testis.
- Genetic testing:In a few cases, we also recommend male genetic testing. One looks like a male, but sometimes there is an extra X in the genetic make-up. For example, as in males with Klinefelter syndrome have XXY. Such male will not have enough sperm or no sperms in their testes.
What Are The Different Male Infertility Treatments In India?
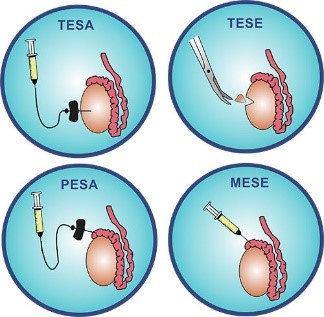
- Male factor infertility includes severe oligospermia, OATs (Oligoasthenoteratozoospermia) and Azoospermia. Dr. Dilip Raja and his team can handle such cases very efficiently.
- If there is a palpable varicocele, we can correct it by microsurgery or laparoscopy. We prescribe gonadotrophins for Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. Here, after the treatment, the sperms produced in the semen are frozen for future use with ICSI.
- If there is no reason found, we give the patient an empirical treatment such as clomiphene, carnitine, coenzyme q, as well as gonadotrophins. After treatment, if the sperm count is 5-10 million/ml, one can undergo 2 IUI cycles followed by ICSI. If the count is less than five mill /ml, it is best to go for ICSI directly.
- In instances of repeated ICSI failure or sperms with a very severe abnormality, one can go for IMSI.
- In case of sperm DNA fragmentation of more than 30 %, one can correct a palpable varicocele if present or give patient oral medication with antioxidants. If DNA fragmentation persists, it is better to do TESE ICSI.
