NOW AVAILABLE AT BREACH CANDY HOSPITAL ON THURSDAYS 11:00 AM TILL 12:00 PM

Dr. Dilip Raja
Urologist & Andrologist
Andrology
In more than 90% of cases, male reproductive disorders have an organic (bodily) cause which can be diagnosed and treated successfully
Get in touch with us today (022) 2645 2007
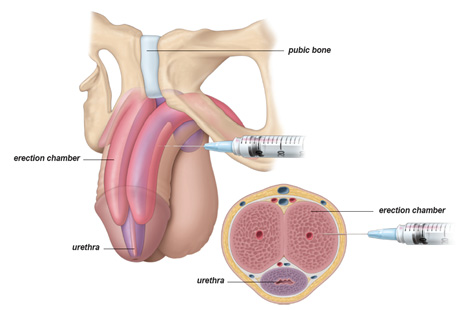
- Andrology is the medical subject that deals with health of male, particularly relating to the problems of the male reproductive system and urologist problems that are unique to men. Andrology also includes the diagnosis of male infertility, therapeutic techniques to improve fertility, embryology services such as in vitro fertilization (IVF) and embryo cryopreservation, consultation services, research into infertility, gamete and embryo banking and patient and health care provider education.
- In more than 90% of cases, male reproductive disorders have an organic (bodily) cause which can be diagnosed and treated successfully – sometimes with medication, at other times with external devices or with surgery. Men are more susceptible to heart disease than women, and tend to have a slightly shorter natural average life span. However, men are more resistant to many conditions that adversely affect women, such as osteoporosis.
- Tremendous progress in basic and clinical research over the past few years has led to a great improvement in our understanding of male reproductive function. Andrology, the branch of medicine that deals exclusively with disorders of the male reproductive system, is the outcome of this research.
- It is the counterpart to gynecology, which deals with medical issues which are specific to women. Thus, Andrology is to the male what gynecology is to the female.
- When faced with infertility, most couples will begin evaluation and therapy with either their gynecologist, a reproductive endocrinologist (female infertility specialist), or an urologist. TheAndrology lab is available to physicians as a reference laboratory to evaluate and assist in the treatment of the couple.
- In general, causes of infertility in men can be explained by deficiencies in ejaculate volume, sperm concentration or too few sperm (oligospermia), complete absence of sperm in the ejaculate (azoospermia), sperm motility (asthenospermia), or sperm morphology (terato- spermia). Nearly 70% of conditions causing infertility in men can be diagnosed by history, physical examination, testicular volume estimation, and hormonal and semen analysis.
- A rational approach is necessary to perform the appropriate work-up and to choose the best treatment options for the couple. It especially affects diabetics (more than 50% of whom are impotent), hypertension, smokers, alcoholics, patients with liver, kidney and heart disease, men who are on medication for unrelated disorders such as hypertension, peptic ulcer or depression (more than 250 drugs are known to cause impotence) etc.
